How to Automate LLM Consistency Validation
Guide to automating LLM consistency checks with self- and cross-validation, key metrics, CI/CD integration, and real-time monitoring.

When deploying language models (LLMs), ensuring consistent outputs is critical. Inconsistent responses can confuse users and erode confidence in your AI product. Manual validation doesn’t scale, making automation a necessity. Here's what you need to know:
- LLM Consistency: Measures how stable and predictable model outputs are when given the same input. It includes:
- Output variance: Tracks response differences.
- Semantic stability: Ensures meaning stays the same, even if wording changes.
- Behavioral reliability: Guarantees dependable responses.
- Why Automate? Manual checks are time-consuming. Automated tools provide real-time monitoring, faster evaluations, and scalability for tasks like regression testing.
- Key Metrics:
- Exact Match: Perfect for tasks like math or API responses.
- Semantic Similarity: Useful for factual queries.
- Lexical Overlap: Ensures consistent phrasing.
- Validation Methods:
- Self-Validation: Tests a model against itself using multiple outputs.
- Cross-Validation: Compares outputs across models using an evaluator model.
- Tools: Platforms like Latitude simplify consistency checks with features like programmatic rules, judge models, and live monitoring.
Main Approaches to LLM Consistency Validation
Consistency validation for language models (LLMs) typically involves two key methods: self-validation and cross-validation. Self-validation focuses on assessing a model's consistency with itself, while cross-validation compares outputs from multiple models. Together, these approaches form the foundation for automated consistency checks in production environments.
Self-Validation Techniques
Self-validation evaluates how consistently a single model generates similar outputs when presented with the same input multiple times. This method, often referred to as internal consistency testing, checks for variations in output to ensure stability and reliability.
One widely used strategy is self-consistency prompting. Here’s how it works: the model generates multiple independent responses to the same prompt, and the final answer is chosen through majority voting. By avoiding greedy decoding, this technique mitigates random errors and explores diverse perspectives to identify the most dependable response.
To implement this, submit the same prompt several times with a temperature setting of 0.6–0.8. Extract the core answer from each response and select the most frequent one. Generally, generating 3–5 samples strikes a good balance between cost and accuracy.
For a more dynamic approach, adaptive self-consistency comes into play. This method evaluates the initial samples and only generates additional ones if necessary. It factors in consensus strength and reasoning diversity to decide when to stop. To optimize costs, early stopping logic can halt sampling as soon as a clear consensus threshold is reached.
Self-validation is particularly effective for deterministic tasks - like solving math problems, answering factual queries, or handling API responses. These tasks benefit from quantitative metrics such as similarity scores and variance measurements. The similarity thresholds should align with the task at hand: use 1.0 for mathematical and API outputs, 0.9 for factual data, and 0.7 for general Q&A.
Cross-Validation with Multiple Models
Cross-validation, on the other hand, focuses on identifying qualitative differences by comparing the outputs of different models.
This method employs a separate model as an independent evaluator, or "judge", to critique the target model's output against specific criteria. Known as the LLM-as-judge framework, it excels at assessing nuanced qualities like tone and clarity that are hard to quantify using simple variance checks.
The judge model uses structured templates to score responses based on predefined criteria. By comparing outputs side-by-side, this method highlights discrepancies and enhances factual accuracy. To minimize subjectivity, it’s essential to develop clear, structured rubrics for the judge model’s evaluations.
For a more comprehensive analysis, combine judge model scores with programmatic rules and human feedback to create a composite consistency score. This approach provides a well-rounded view, addressing both quantitative and qualitative aspects of consistency.
Tools and Metrics for Consistency Validation
LLM Consistency Validation Metrics and Thresholds Guide
Ensuring consistency in outputs requires a combination of quantitative metrics and automated tools. The right approach depends on the type of output you're dealing with - whether it's structured data like JSON or more nuanced elements like tone. These tools and metrics serve as the bridge between theoretical evaluation methods and automated, practical applications.
Common Metrics for Consistency Evaluation
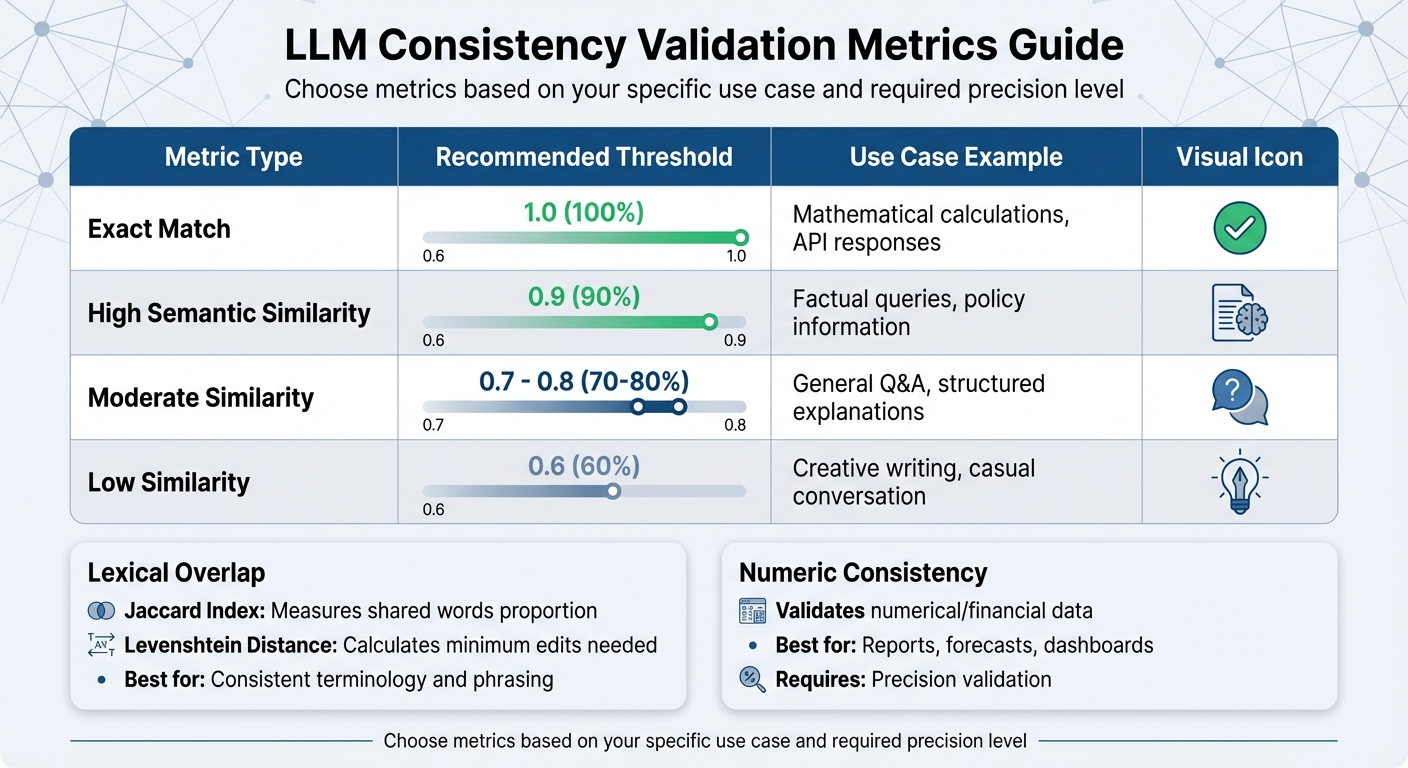
Exact Match is the most rigid metric, demanding a 100% match between outputs. This is particularly useful for tasks like pricing calculations or mathematical operations, where even the smallest deviation can signal a problem. A threshold of 1.0 is standard for these cases.
Semantic Similarity evaluates how closely two outputs align in meaning, even if their wording differs. This metric relies on embedding models, such as text-embedding-3-small, to assess conceptual overlap. It's especially effective for factual queries where the same idea might be expressed in various ways. A threshold of 0.9 works well for factual content, while 0.7 is more suitable for general Q&A scenarios.
Lexical Overlap metrics, like the Jaccard Index and Levenshtein Distance, focus on word-level and structural similarities. The Jaccard Index measures the proportion of shared words between two outputs, while Levenshtein Distance calculates the minimum edits needed to transform one string into another. These metrics are ideal for ensuring consistent terminology and phrasing.
For outputs involving numbers, numeric consistency checks are critical. These specialized methods validate numerical or financial data, which is essential for applications like reports, forecasts, or dashboards where precision is non-negotiable.
| Metric Type | Recommended Threshold | Use Case Example |
|---|---|---|
| Exact Match | 1.0 | Mathematical calculations, API responses |
| High Semantic Similarity | 0.9 | Factual queries, policy information |
| Moderate Similarity | 0.7 - 0.8 | General Q&A, structured explanations |
| Low Similarity | 0.6 | Creative writing, casual conversation |
Using Latitude for Consistency Validation
To put these metrics into action, frameworks like Latitude simplify the process of validating consistency in real-world scenarios. Latitude is an open-source evaluation framework that supports the entire consistency validation lifecycle through three key approaches: LLM-as-Judge, Programmatic Rules, and Human-in-the-Loop review.
Programmatic Rules involve automated, code-based checks to validate objective criteria. These are perfect for ensuring structural consistency, such as verifying JSON schema compliance, regex patterns, or length constraints. For example, if an LLM generates product recommendations in JSON format, programmatic rules can immediately identify malformed responses before they reach users.
LLM-as-Judge uses a secondary model to assess subjective qualities like tone. This method is particularly effective for identifying inconsistencies that traditional metrics might miss, such as shifts from formal to casual language or contradictory advice across similar queries.
Latitude also offers two operational modes: Batch Mode for regression testing with golden datasets and Live Mode for real-time monitoring. Both enhance the reliability of consistency checks.
One standout feature of Latitude is its Composite Evaluations, which combine multiple metrics into a single score. For instance, you could merge exact match scores, semantic similarity ratings, and judge model assessments to get a broad view of consistency. Additionally, you can flag certain evaluations, such as toxicity or hallucination checks, as "negative", prompting the system to minimize these scores.
Latitude's AI Gateway automatically logs all interactions - inputs, outputs, and performance metrics - eliminating the need for manual logging setup. For teams with existing infrastructure, Latitude's Python and TypeScript SDKs make it easy to run prompts locally and push logs back for evaluation.
For more complex outputs, Latitude's Advanced Configuration allows you to focus on specific fields within a response. For instance, instead of evaluating an entire JSON output, you can target specific elements, such as arguments.recommendations[1], to ensure consistency at a granular level.
Setting Up Automated Consistency Validation in Production
To maintain consistent performance, it's essential to integrate validation processes into both development and production workflows. By embedding these checks, you can catch issues early - before users are affected. Unlike traditional software testing, working with large language models (LLMs) involves handling non-deterministic outputs, so you'll rely on thresholds instead of binary pass/fail criteria.
Adding Validation to CI/CD Pipelines
Start by building a golden dataset of real-world test cases. This dataset will serve as the foundation for your validation process. Then, define evaluators using a mix of approaches:
- Programmatic rules: For objective checks like JSON schema validation.
- LLM-as-Judge: For subjective criteria, such as assessing tone or style.
Set specific assertions, such as correctness_score > 0.9, and integrate these tests into your CI/CD pipeline using tools like GitHub Actions or CircleCI. This setup ensures that deployments failing to meet your benchmarks are automatically blocked.
Additionally, make sure API keys are securely stored in your CI/CD settings. This step allows the pipeline to access models during the testing phase without compromising security.
Real-Time Monitoring and Reporting
Once validation is part of your CI/CD pipeline, the next step is to implement real-time monitoring to keep tabs on the model's behavior in production. While CI/CD addresses pre-deployment issues, live monitoring helps identify problems that arise after deployment.
Enable automated evaluations on production logs. Since production data often lacks ground truth labels, focus on reference-free evaluators, such as:
- LLM-as-Judge
- Programmatic rules
- Quality heuristics that don't rely on predefined outputs.
Set up automated alerts to notify your team of performance dips. For more in-depth analysis, use batch pipelines to periodically fetch production traces, run evaluations, and update a central dashboard with performance scores.
To manage costs, consider sampling evaluations instead of running them on every interaction. This is especially important when using judge models. Track statistical metrics like mean variance and standard deviation to spot when your model's behavior becomes less predictable over time. Finally, include failing or edge-case production traces in your golden dataset to refine and improve your model continuously.
Best Practices for Consistency Validation
When it comes to ensuring your product's validation remains strong after deployment, it's not just about automated testing. The key lies in adopting practical strategies that adapt and grow alongside your product.
Continuous Improvement Through Feedback
Start by setting clear quality benchmarks before deployment. Define specific metrics - like accuracy, tone, and safety - and establish minimum acceptance scores that every output must meet.
The real magic happens when you dive into production data. Regularly review logs with poor evaluation scores to pinpoint root issues. Use tools like automated prompt suggestions to refine your approach. When you come across tricky edge cases or particularly successful outputs, add them to your golden dataset. This ensures your benchmarks stay relevant and robust.
By leveraging these insights, you build a foundation for strict version control and consistent testing.
Version Control and Iterative Testing
Treat prompt and validation criteria updates like software code - version them meticulously. Keep detailed records of changes to create an audit trail, and always batch-test updates against your golden dataset to prevent regressions.
Introduce a review process where team members test changes in a draft environment before they go live. For critical metrics like safety and helpfulness, enable live evaluations to catch any consistency issues as soon as they arise. Combining pre-deployment testing with real-time monitoring creates a multi-layered safety net that minimizes risks.
This structured approach to versioning and testing ensures teams can work together seamlessly to enhance validation.
Team Collaboration Workflows
Consistency validation thrives on collaboration. Developers, product managers, and domain experts should work hand-in-hand throughout the development process. Regular review meetings are a great way to analyze evaluation trends and dig into failure logs.
Make evaluation results a core part of the peer review process, especially for outputs that miss the mark. Using composite scores can simplify performance summaries for stakeholders, turning consistency validation into a shared responsibility instead of something left solely to developers.
Conclusion
Ensuring consistency through automated validation is the backbone of dependable AI systems. When an AI delivers inconsistent answers to the same question, it undermines the reliability essential for enterprise-level applications. Addressing this challenge lays the groundwork for measurable improvements in performance.
Using tools like GPT-5 for automated validation achieves over 95% accuracy in syntax checks, while applying predicate logic enhances error recall by 16–50 percentage points in regulatory and mathematical tasks. This distinction separates dependable AI systems from those that pose risks.
But it’s not just about numbers. Structured workflows enable scalability. By combining batch testing with real-time monitoring - building on the earlier discussion of golden datasets - you create a multi-layered safety net that identifies issues before they reach end-users. Platforms like Latitude offer this continuous workflow, covering everything from design to deployment and ongoing refinement. This approach transforms validation from a one-off task into a continuous cycle of improvement.
Consistency validation should be a shared responsibility across teams. As highlighted in earlier best practices, fostering collaboration ensures ongoing progress. Integrating automated checks into your CI/CD pipeline, enabling live evaluations for critical metrics, and maintaining version control for every update builds systems that evolve and improve with time. The aim isn’t perfection from the start - it’s about creating a framework that learns and adapts.
Start automating early and expand your validation processes as your AI product grows. This is how experimental features evolve into production-ready solutions that deliver reliable, scalable results.
FAQs
What are the advantages of using self-validation compared to cross-validation for ensuring LLM consistency?
When evaluating the consistency of large language models (LLMs), self-validation and cross-validation each bring distinct benefits to the table.
Self-validation involves the model assessing its own outputs based on its internal reasoning and confidence levels. This method works well for automating checks on large datasets or outputs, thanks to its efficiency and scalability. It also shines in production settings, where it enables real-time monitoring and ongoing improvements without relying on external reviewers.
Meanwhile, cross-validation takes a different approach by comparing the model's outputs to external benchmarks or even other models. This ensures evaluations are more objective, aligning the results with broader standards and helping to minimize the risk of overfitting.
For a well-rounded validation process, combining these methods can be highly effective. Self-validation delivers speed and scalability, while cross-validation adds a layer of rigor and impartiality. Together, they create a balanced approach to assessing LLM performance.
How do automated tools help scale LLM consistency validation?
Automated tools simplify the task of validating consistency in large language models (LLMs), making the process faster and less reliant on manual work. These tools can handle massive datasets, generate responses automatically, and quickly identify inconsistencies in outputs.
For example, platforms like Latitude offer structured workflows to track model behavior, gather human feedback, and conduct evaluations. They also enable advanced techniques such as self-validation and cross-model comparisons to ensure consistent performance over time. By automating these steps, teams can uphold dependable, high-quality LLM outputs, even in large-scale production settings.
What are the key metrics for validating different types of LLM outputs?
When evaluating outputs from large language models (LLMs), it's essential to use metrics that match the type of content you're reviewing. For responses rooted in facts or knowledge, focus on self-consistency - this ensures the model consistently provides the same answer to identical prompts. Additionally, check for semantic similarity to verify that responses, even when worded differently, still convey the intended meaning.
For more creative outputs, like summaries, conversational replies, or storytelling, prioritize contextual relevance and structural coherence. These help ensure the response aligns with the prompt and maintains a logical flow. It's also important to apply contradiction detection to spot and address any conflicting information within the output.
Ultimately, the choice of metrics should reflect the type of content and the qualities you're aiming for - whether it's accuracy, coherence, or logical consistency. Tailoring the validation process to the specific use case ensures more reliable and relevant assessments.

