Dynamic Prompt Behavior: Key Testing Methods
How teams use batch testing, live evaluation, A/B tests, and automated optimization loops to validate and improve dynamic prompts for reliable LLM behavior.

Dynamic prompts let AI systems respond to context, user interactions, and live data, unlike static prompts that deliver fixed outputs. Testing these prompts is critical because they can fail unpredictably due to silent API updates or changing user inputs. Here’s how teams test and refine dynamic prompts to ensure reliability:
- Batch Testing: Uses predefined datasets to catch errors and validate updates.
- Live Evaluation: Monitors production logs to spot issues like safety concerns or performance drift.
- A/B Testing: Compares different prompt versions using real user traffic to improve outcomes.
- Automated Optimization Loops: Continuously refines prompts based on feedback and metrics.
Each method targets specific challenges, like stability, user experience, or long-term improvements. Combining these approaches ensures prompts remain effective and responsive to evolving needs.
Testing Methods for Dynamic Prompts
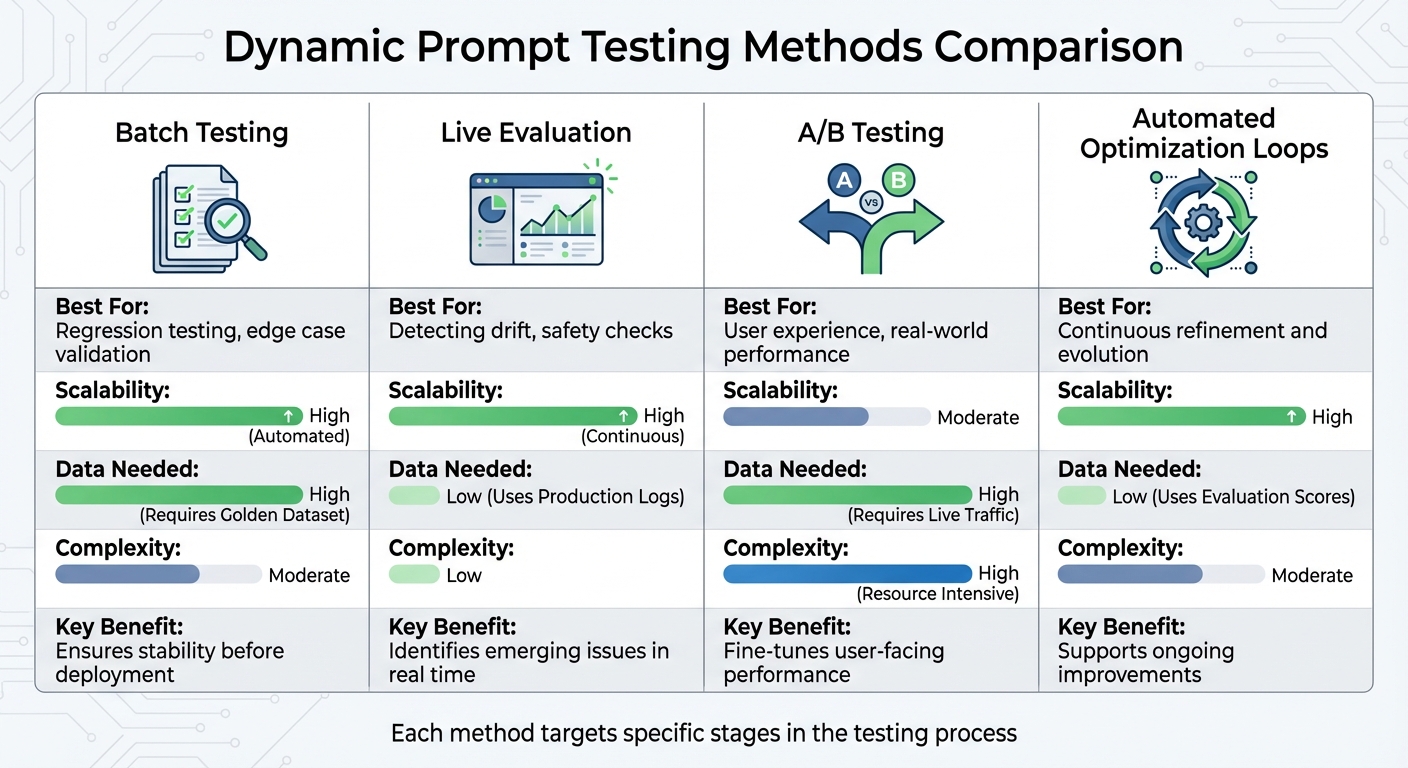
Comparison of Four Dynamic Prompt Testing Methods: Strengths and Requirements
Testing dynamic prompts effectively requires a structured approach that adapts to their ever-changing nature. Teams typically rely on four key methods: batch testing, live evaluation, A/B testing, and automated optimization loops. Each method addresses specific challenges, ensuring prompt reliability and adaptability.
Batch testing involves running evaluations against a predefined "golden dataset" of inputs and expected outputs. This is particularly effective for regression testing, ensuring that updates to prompts don't disrupt existing functionality. It's especially useful when working with metrics that rely on ground truth data, such as Semantic Similarity or Exact Match.
Live evaluation focuses on continuously monitoring production logs. This method is invaluable for identifying safety issues, unexpected user inputs, and performance regressions, especially when silent updates to models occur.
A/B testing compares different versions of prompts, model configurations (like GPT-4 versus Claude), or parameter settings using live traffic. As Francesco Alaimo, Team Lead at TIM, explains:
Effective prompt engineering is usually not a static, one-time interaction. It's a learning process where testing and refining your prompts is essential.
Automated optimization loops close the feedback loop by using evaluation results - whether from AI scoring, programmatic rules, or human reviews - to suggest and refine prompts iteratively. This reduces manual effort while maintaining quality across production environments. Together, these methods create a robust framework for ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of dynamic prompts.
Comparison of Testing Methods
The table below highlights the strengths and requirements of each method:
| Method | Best For | Scalability | Data Needed | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Testing | Regression testing, edge case validation | High (Automated) | High (Requires Golden Dataset) | Moderate |
| A/B Testing | User experience, real-world performance | Moderate | High (Requires Live Traffic) | High (Resource Intensive) |
| Live Evaluation | Detecting drift, safety checks | High (Continuous) | Low (Uses Production Logs) | Low |
| Automated Optimization Loops | Continuous refinement and evolution | High | Low (Uses Evaluation Scores) | Moderate |
Each method is suited to a specific stage in the testing process. Batch testing ensures stability before deployment, live evaluation identifies emerging issues in real time, A/B testing fine-tunes user-facing performance, and automated optimization loops support ongoing improvements. The challenge lies in selecting the right method based on your validation goals.
Batch Testing for Prompt Validation
Batch testing is a method used to evaluate dynamic prompts against predefined datasets, ensuring quality and reliability before deployment. Poorly constructed prompts can lead to inconsistent AI performance, eroding user trust and derailing projects. This approach relies on golden datasets - carefully designed collections of inputs paired with expected outputs that reflect both common scenarios and edge cases.
When you test prompts with these datasets, you can gauge their effectiveness using metrics like adherence to JSON schema, keyword matching, and response clarity. This is especially useful for regression testing, which ensures updates to prompts don’t disrupt existing functionality.
Batch testing is critical for catching issues that manual reviews might miss, such as hallucinations, factual errors, or formatting problems like invalid JSON or missing tags. Studies show that using batch testing to validate dynamic workflows can reduce errors in multi-step processes by over 30%.
Automated test suites often focus on key performance indicators, such as achieving accuracy levels above 95% and maintaining latency under 2 seconds. Monitoring these metrics over time helps teams detect "model drift", where performance subtly declines due to changes in models or new edge cases in production data.
By following a structured, metrics-driven process, batch testing provides a reliable way to maintain prompt consistency and effectiveness.
Steps for Batch Testing
-
Prepare Your Dataset
Start by uploading a CSV file, generating synthetic cases, or pulling real-world logs. Include anexpected_outputcolumn to measure metrics like Semantic Similarity or Exact Match, which require ground truth data. -
Define Evaluation Criteria
Set clear metrics for evaluation. For subjective qualities like tone or helpfulness, use LLM-as-a-judge, where another model scores the outputs. For objective checks, use programmatic rules like JSON schema validation, regex patterns, or keyword matching. Establish a minimum passing score to determine readiness for production. -
Run the Tests
Execute the batch run by testing your prompt variants against the dataset. If your prompt involves tool calling or JSON mode, configure field accessors (e.g.,arguments.recommendations[19]) to target specific response elements. -
Analyze Results
Review aggregated statistics, success rates, and score distributions. Tools like Latitude offer features such as "Run History" to track accuracy trends and "Session Replays" to examine prompt behavior with specific inputs. Compare results across runs to identify patterns or areas for improvement. -
Refine and Retest
Use insights from failed test cases to improve your prompts, then re-run the tests until you meet the desired score thresholds. Perform these tests daily or whenever prompts are updated to catch issues early. This ongoing validation ensures your prompts remain dependable as they evolve.
Batch testing, when done consistently, supports the creation of reliable and efficient prompts, helping teams maintain high-quality outputs even as demands shift.
A/B Testing for Prompt Optimization
A/B testing takes the concept of batch testing a step further, allowing you to fine-tune prompt performance based on real-world user interactions. By splitting user traffic between different prompt versions, you can directly compare their effectiveness in a live environment. Typically, this starts with an even 50/50 traffic split between the original prompt (control) and a new variation. Deterministic hashing ensures users are consistently assigned to the same version, while tools like HAProxy manage this routing for an unbiased comparison.
When running A/B tests, focus on three main metrics: Technical Performance (like response time, F1 score, and accuracy), User Experience (such as satisfaction ratings and session duration), and Business Impact (including retention rates, token usage, and costs). For instance, teams often aim for at least a 10% improvement in F1 scores over the baseline. Meanwhile, engagement metrics like click-through rates might be monitored hourly to track immediate user behavior. To ensure reliable results, conduct a power analysis to confirm your sample size is statistically significant. Once a "winning" variant is identified, roll it out gradually using feature flags - starting with 10% of traffic and scaling up to 25%, 50%, and finally 100% - to confirm consistent performance before full deployment.
Using Observability for A/B Testing
Observability tools are invaluable for monitoring A/B tests in real-time, offering insights into how your prompts perform in production. For example, Latitude's Live Mode automatically scans production logs to assess quality factors like safety and helpfulness, eliminating the need for manual checks. Additionally, the platform's Experiments feature provides side-by-side visual comparisons of key metrics - such as accuracy, cost, duration, and token usage - making it easier to evaluate how different prompt versions stack up.
Automated Optimization Loops for Prompt Refinement
A/B testing might help you compare different prompt versions, but automated optimization loops take it a step further. These loops refine prompts continuously, all while minimizing the need for manual input. They follow a cycle: Design → Test → Deploy → Monitor → Evaluate → Improve, using feedback from real-world performance to adjust and improve prompts. The key lies in choosing the right evaluation methods to act as "reward signals." These can include an LLM-as-Judge scoring qualities like tone and helpfulness, programmatic rules ensuring format compliance, or human-in-the-loop feedback capturing more nuanced preferences.
The results? Pretty impressive. Iterative prompt refinement has been shown to increase AI model accuracy by 30% and reduce bias by 25%. But to make this work, you need clear success metrics from the start. Start by building a "Golden Dataset" to serve as your baseline. Then, combine various evaluation methods into a single "Composite Score" to guide the optimization loop. This structured approach is the backbone of dynamic prompt systems that improve over time.
Platforms like Latitude's Live Mode take this further by analyzing production logs in real time to suggest prompt adjustments. Its Prompt Suggestions feature gathers scores, labels, and feedback to recommend specific refinements based on past performance patterns.
"Effective prompt engineering is usually not a static, one-time interaction. It's a learning process where testing and refining your prompts is essential." – Francesco Alaimo, Team Lead, TIM
Another powerful tool? Configuring optimization loops for "negative evaluations." Instead of focusing solely on maximizing positive scores, these loops target reducing unwanted traits like toxicity or hallucinations.
Reinforcement Learning for Prompt Evolution
Reinforcement learning builds on these optimization loops by introducing a self-improving mechanism. The system generates variations of a prompt, tests them with real inputs, evaluates the outputs based on your chosen metrics, and feeds that feedback back into the loop. This creates a cycle where prompts get better with each iteration.
The evaluation results act as reward signals. For subjective criteria, LLM-as-Judge evaluations can be used. For more objective checks - like ensuring JSON format compliance, checking for specific keywords, or controlling response length - programmatic rules are ideal. Human-in-the-loop feedback is invaluable for capturing nuanced preferences and creating those all-important Golden Datasets.
For instance, using self-correction prompting with GPT-4 has shown an 8.7% increase in accuracy for specific tasks and a 13.9-unit improvement in code readability. Combining few-shot learning with chain-of-thought prompting has boosted performance in sentiment reversal tasks by 21.6 units. The trick is running enough iterations with large enough sample sizes to ensure meaningful results, not just random fluctuations.
For advanced setups, PromptL syntax can introduce variables, conditionals, and loops directly into prompts. This allows prompts to adapt dynamically based on the feedback they receive, enabling more responsive behavior. Tracking inputs, outputs, and metadata is crucial for pinpointing exactly where and why a prompt isn't performing as expected.
Meta-Prompting and Dynamic Selection
Meta-prompting takes automation to another level by enabling systems to generate and select their own optimized prompt variations. Instead of writing every variation manually, you create a high-level "meta-prompt" that defines the structure and criteria for effective prompts. The LLM then generates candidate prompts based on these guidelines.
Once generated, these variations are evaluated, and performance feedback informs the next generation cycle. For example, a zero-shot meta-prompted Qwen-72B model achieved 46.3% accuracy on the MATH benchmark, surpassing GPT-4's initial version, which scored 42.5%.
Dynamic selection brings this concept into real-world applications. Instead of sticking with the same prompt template for every query, a meta-controller or lightweight neural network selects the best prompt configuration for each specific input at runtime. Dynamic In-Context Learning (DynaICL) has demonstrated up to 46% token savings while delivering a 2.6% absolute accuracy gain compared to static prompts. For Retrieval-Augmented Generation tasks, meta-prompting optimization has shown accuracy improvements of up to 33% over standard RAG methods.
Latitude supports these workflows with its AI Gateway, which deploys prompts as API endpoints, and an evaluation framework for running LLM-as-Judge or programmatic rules against production logs. This setup allows you to track which prompt versions perform best over time, making it easier to fine-tune and improve. You can even compare key metrics - like accuracy, cost, duration, and token usage - side by side to evaluate different configurations.
"The LLM becomes a meta-designer of its own behavior." – Raji Rai
When implementing meta-prompting, it's useful to include contrastive examples. Ask the LLM to compare good outputs against bad ones to identify failure patterns and success factors. Striking the right balance is critical - optimized prompts need to provide enough context to remain relevant but shouldn't be so restrictive that they fail when faced with new, unseen data. The ultimate aim is to create a system that continuously learns and adapts, rather than relying on one-time fixes.
Conclusion
Testing dynamic prompts is a critical step in ensuring the reliability of large language model (LLM) applications. By combining batch testing with golden datasets, A/B testing, and automated optimization loops, you can address key challenges in maintaining and improving performance. Batch testing helps maintain stability, A/B testing provides measurable insights into the effects of changes, and automated loops allow for continuous adaptation to user needs - all working together to create a solid foundation for handling evolving demands.
It's worth noting that prompts that once worked effectively may no longer perform as expected due to changing conditions. LLM APIs often update quietly, altering behaviors in ways that traditional software testing might miss. That's why a mix of evaluation methods is essential for creating a reliable safety net.
"Stable outputs come from slice-level regression tests, frequent production sampling, and rollouts gated by flags and experiments." – Statsig
To build on these methods, start by defining clear metrics that align with your technical goals (e.g., improving F1 scores by 10%), user satisfaction, and business objectives. Gradual rollouts using feature flags - starting with 10% of users, then increasing to 25%, 50%, and eventually 100% - can help catch potential issues before they impact everyone. Pay close attention to slice-level analysis, as regressions often occur in specific user groups or content types. This iterative, lifecycle-driven approach ensures that prompts evolve to meet new requirements.
Latitude simplifies these testing processes with tools like integrated batch evaluations, live monitoring, and A/B testing. Its AI Gateway allows you to deploy prompts as API endpoints, while its evaluation framework tracks performance through production logs. This makes it easier to identify successful prompt variants and maintain consistent quality over time.
FAQs
What is the difference between batch testing and live evaluation for dynamic prompts?
Batch testing and live evaluation offer two different approaches to assessing dynamic prompts.
Batch testing works by running a fixed set of prompts against a static dataset. This makes it perfect for controlled, repeatable evaluations. It’s a great way to systematically pinpoint issues without the unpredictability that comes with real-time inputs.
In contrast, live evaluation involves testing prompts with real-time user inputs. This method provides a window into how prompts perform in actual, dynamic scenarios. However, the unpredictability of live inputs can make diagnosing problems trickier.
Both methods bring unique strengths to the table and can be combined to ensure prompts perform effectively across different situations.
How does A/B testing enhance the performance of AI prompts?
A/B testing is a powerful way to compare different versions of a prompt to determine which one delivers better results. By establishing clear success metrics - such as accuracy, response time, or user satisfaction - you can evaluate how adjustments in wording, temperature settings, or tool configurations influence the AI’s responses. This method uncovers potential issues that might not surface during isolated testing, helping teams fine-tune prompts for more natural and efficient interactions.
When used within platforms like Latitude, A/B testing can easily scale to production environments. It enables thorough experimentation by collecting both quantitative data and qualitative insights. This approach ensures that only the most effective prompts are implemented to enhance the user experience, while underperforming ones are either improved or discarded. The outcome is a more reliable and user-focused AI system.
How do automated optimization loops improve dynamic prompts?
Automated optimization loops work by analyzing the outputs of dynamic prompts and tweaking them step by step to improve both accuracy and relevance. Essentially, it's a cycle of learning and adjusting that keeps refining the prompts.
By spotting patterns and fine-tuning parameters based on how well they perform, these loops help prompts evolve to handle different contexts more effectively. Over time, this leads to more precise and dependable outcomes.

