Open-Source Platforms for LLM Evaluation
Compare open-source LLM evaluation platforms that add observability, automated metrics, and CI/CD testing to reduce hallucinations and production errors.

Evaluating large language models (LLMs) is critical to ensure their reliability, accuracy, and safety. Open-source tools have emerged as a practical solution for teams building AI products, offering transparency, cost savings, and flexibility. These platforms enable teams to test LLMs for issues like hallucinations, bias, and toxicity before they impact users. Here's what you should know:
- Why It Matters: Businesses lose ~$1.9 billion annually due to undetected LLM failures. Regular testing can prevent such losses and improve performance.
- Key Benefits:
- Transparent and reproducible testing.
- Vendor-neutral tools for comparing multiple LLMs.
- Customizable metrics for specific use cases.
- Cost savings on development (up to $500,000 annually).
- Popular Platforms:
- Latitude: Focuses on production monitoring and prompt optimization with features like LLM-as-Judge, programmatic rules, and human-in-the-loop workflows.
- DeepEval: Integrates with CI/CD pipelines and offers 50+ metrics for testing correctness, relevance, and more.
- Arize Phoenix: Provides observability and debugging through OpenTelemetry.
- Langfuse: Tracks LLM performance in production with call traceability and A/B testing.
- LM Evaluation Harness: A framework for academic benchmarking, powering the Hugging Face Open LLM Leaderboard.
Quick Tip: Start by adding observability to monitor inputs and outputs, then expand into more advanced evaluation methods. Open-source tools like Latitude and DeepEval can help teams reduce errors and improve LLM accuracy by up to 30% in weeks.
Latitude: Open-Source AI Engineering Platform
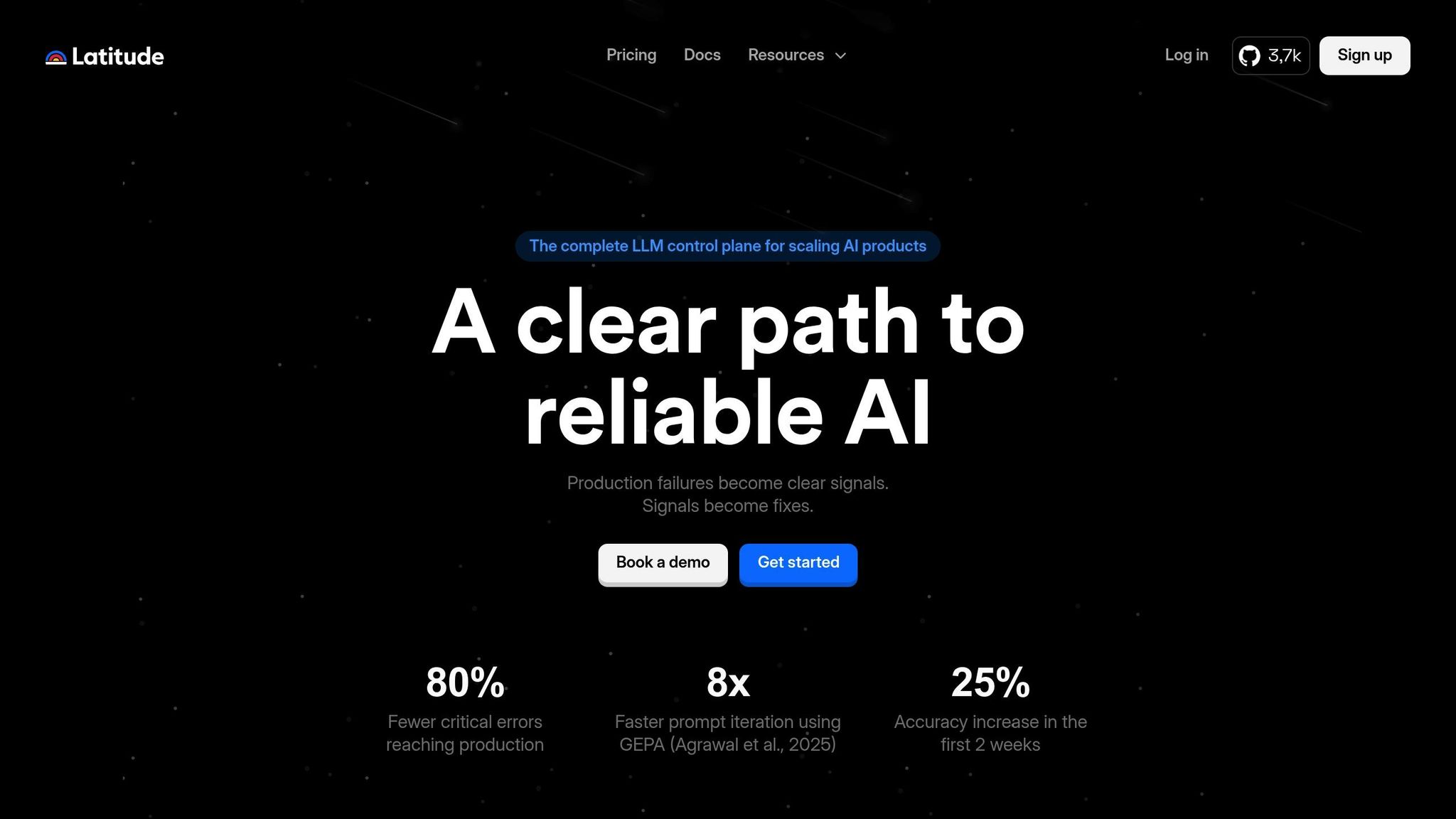
Latitude is an open-source platform designed to manage the entire lifecycle of AI products. It introduces a "Reliability Loop", which captures production traffic, incorporates human feedback, identifies and groups failures, runs regression tests, and automates prompt adjustments to improve performance.
Main Features
Latitude includes a Prompt Manager powered by PromptL, a specialized language that supports variables, conditionals, and loops for advanced prompt handling. Teams can version control and collaborate on prompts just like they do with code. These prompts are then deployed as API endpoints through the AI Gateway, which automatically syncs with published changes, eliminating the need for manual deployments.
The platform offers three evaluation methods:
- LLM-as-Judge: Evaluates subjective aspects like tone and clarity.
- Programmatic Rules: Handles objective checks using tools like regex, JSON validation, or exact match.
- Human-in-the-Loop: Allows manual scoring to build "golden datasets."
Evaluations can run in two modes: Batch Mode for regression testing on datasets or Live Mode for real-time monitoring. Teams using Latitude have reported an 80% drop in critical errors reaching production and a 25% boost in model accuracy within just two weeks of adoption.
These features make it easier for both technical and non-technical teams to enhance LLM performance in production environments.
How Product and Engineering Teams Use Latitude
Latitude brings together product managers, engineers, and domain experts. Product teams can monitor live traffic, provide feedback, and flag issues - all without needing to touch the code. Engineers can take this input to run automated evaluations and monitor quality metrics over time. The platform's Prompt Optimizer, which leverages GEPA (Agrawal et al., 2025), enables 8x faster prompt iteration by automatically testing variations.
Latitude integrates seamlessly with major providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure, Google Vertex AI, Amazon Bedrock, and Mistral. It also supports frameworks such as the Vercel AI SDK, LangChain, and LiteLLM. Additionally, teams can use OTEL-compatible telemetry to collect production data without altering their application logic.
Common Use Cases
Latitude simplifies debugging with automatic failure grouping, supports A/B testing to compare prompt versions on identical datasets, and enables regression tests to ensure consistent functionality. Its Live Mode offers real-time insights into quality, all without requiring ground truth data.
The platform is available in two forms: Latitude Cloud, a managed solution, and Latitude Self-Hosted, an open-source option under the LGPL-3.0 license for private infrastructure. With over 3.7k stars on GitHub, Latitude has become a go-to choice for teams looking for transparent and customizable LLM evaluation workflows.
Other Open-Source Platforms for LLM Evaluation
In addition to Latitude's platform, several open-source tools offer unique methods for evaluating large language models (LLMs). Here's a closer look at some of these options:
DeepEval
DeepEval is a Pytest-style framework that integrates LLM evaluations directly into CI/CD pipelines. It includes more than 50 research-backed metrics (like G-Eval, DAGA, and QAG) to measure aspects such as correctness, consistency, relevance, and even hallucination detection. The platform also supports multi-modal evaluations, manages single and multi-turn conversations, and allows users to create custom metrics. On top of being free, it offers a cloud-based collaborative testing environment through Confident AI. Other tools in this space also focus on observability and monitoring in production settings.
Arize Phoenix
Arize Phoenix uses OpenTelemetry to provide vendor-neutral observability and troubleshooting. With over 2.5 million downloads and a community of 7,000+ members, it has become a popular choice. One of its standout features is the use of embeddings for semantic clustering, which helps identify patterns in problematic responses, particularly in complex, multi-step LLM workflows. Jerry Liu, CEO and Co-Founder of LlamaIndex, highlighted its importance:
"As LLM-powered applications increase in sophistication... deeper capabilities around LLM observability are needed to help debug and troubleshoot. We're pleased to see this open-source solution from Arize".
Arize Phoenix is entirely open source, self-hostable, and comes with no feature restrictions.
Langfuse
Langfuse focuses on monitoring LLM performance in production environments. It offers full call traceability, prompt versioning, and even LLM-as-judge evaluations. Its dashboards are tailored for A/B testing and benchmarking, making it easy for teams to compare different prompt engineering concepts and track improvements across deployments.
Language Model Evaluation Harness
EleutherAI's Language Model Evaluation Harness serves as the backbone for the Hugging Face Open LLM Leaderboard, providing a framework for reproducible LLM testing. With 11.2k stars and 3k forks on GitHub, it supports more than 60 academic benchmarks and offers a unified command-line interface with YAML-based configuration. Stella Biderman, Executive Director at EleutherAI, described its significance:
"The LM Evaluation Harness [is] a unifying framework that allows any causal language model to be tested on the same exact inputs and codebase".
This tool is free under the MIT license and works seamlessly with local models, commercial APIs, and specialized hardware backends.
Feature Comparison
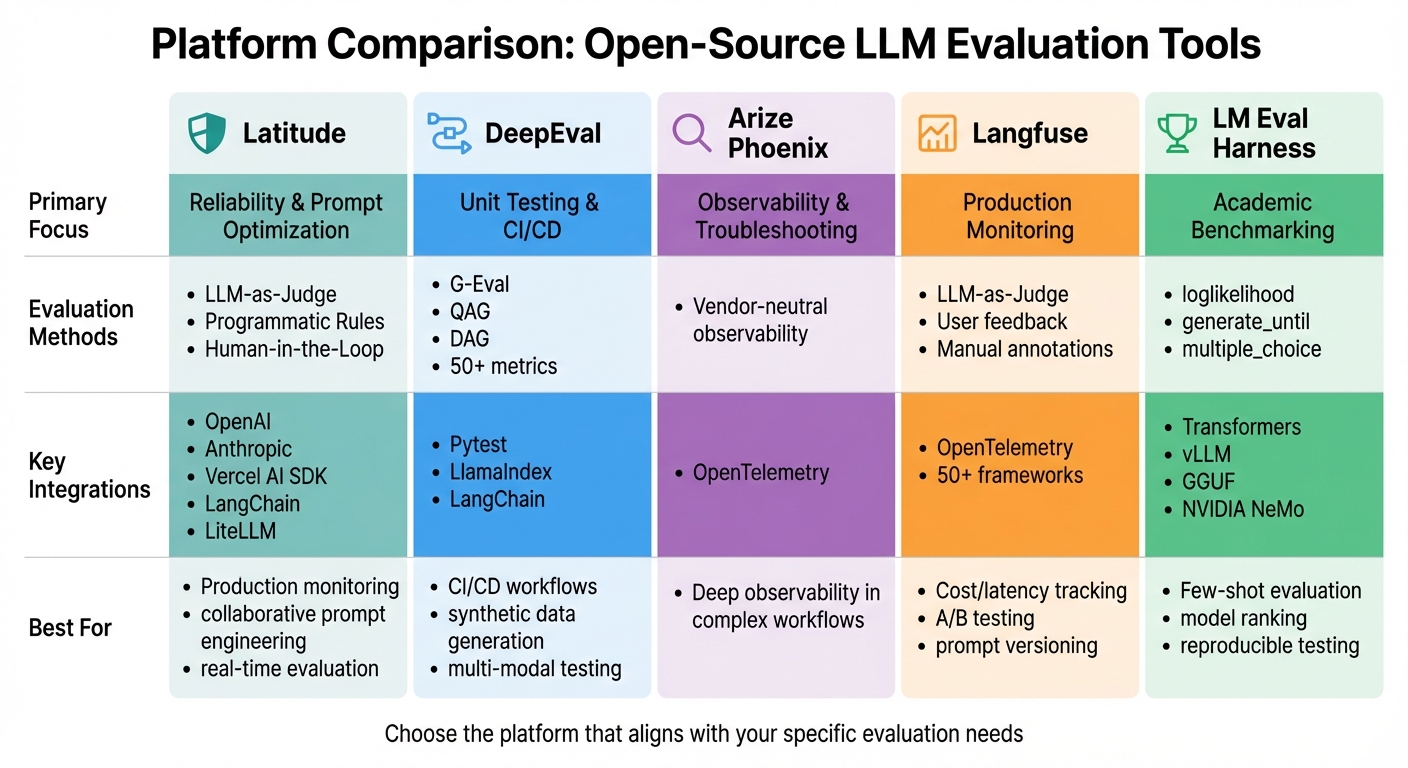
Open-Source LLM Evaluation Platforms Comparison: Features and Best Use Cases
Each platform brings a unique approach to evaluating large language models (LLMs), allowing you to choose the tool that aligns best with your specific requirements. Here's a breakdown of their core features and evaluation methods to help you make an informed decision.
Latitude employs a reliability loop that combines observability, human feedback, and automated tests. This method helps teams cut critical errors by 80% and iterate eight times faster using GEPA (Agrawal et al., 2025). It supports LLM-as-Judge, programmatic rules, and human-in-the-loop workflows, making it ideal for aligning production monitoring with prompt optimization.
DeepEval integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines through Pytest. It offers over 50 research-backed metrics (G-Eval, QAG, DAG) and generates synthetic data for comprehensive test cases.
LM Evaluation Harness is tailored for academic benchmarking and serves as the backbone of the Hugging Face Open LLM Leaderboard.
Lighteval stands out by supporting more than 1,000 evaluation tasks across various backends, including vLLM and SGLang.
Platform Comparison Table
| Platform | Primary Focus | Evaluation Methods | Key Integrations | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | Reliability & Prompt Optimization | LLM-as-Judge, Programmatic Rules, Human-in-the-Loop | OpenAI, Anthropic, Vercel AI SDK, LangChain, LiteLLM | Production monitoring, collaborative prompt engineering, real-time evaluation |
| DeepEval | Unit Testing & CI/CD | G-Eval, QAG, DAG, 50+ metrics | Pytest, LlamaIndex, LangChain | CI/CD workflows, synthetic data generation, multi-modal testing |
| Arize Phoenix | Observability & Troubleshooting | Vendor-neutral observability | OpenTelemetry | Deep observability in complex workflows |
| Langfuse | Production Monitoring | LLM-as-Judge, User feedback, Manual annotations | OpenTelemetry, 50+ frameworks | Cost/latency tracking, A/B testing, prompt versioning |
| LM Eval Harness | Academic Benchmarking | loglikelihood, generate_until, multiple_choice | Transformers, vLLM, GGUF, NVIDIA NeMo | Few-shot evaluation, model ranking, reproducible testing |
Conclusion
The Role of Open-Source LLM Evaluation
Open-source evaluation platforms have become a cornerstone for teams aiming to create reliable AI systems. Stella Biderman, Executive Director at EleutherAI, highlights their importance:
"Quantifying the performance of large language models is crucial to evaluating new techniques and validating new approaches so that different model releases can be compared objectively".
These platforms ensure trustworthy and repeatable evaluations by inherently capturing software provenance, even across varying environments. Unlike proprietary tools, open-source frameworks offer teams complete control over their data and infrastructure, a critical factor for enterprise-level security. They also allow for deep debugging and customization, enabling teams to analyze individual samples, pinpoint specific failures, and design metrics tailored to their unique business needs. Additionally, the customizable benchmarks provided by these platforms make it easier to ensure results are comparable across different organizations.
The collaborative nature of open-source tools drives faster advancements. A great example is the LM Evaluation Harness, which powers the Hugging Face Open LLM Leaderboard and is widely used by organizations like NVIDIA, Cohere, and Mosaic ML. This collective use creates a feedback loop, where improvements benefit the entire community.
Taking the First Steps
The advantages of these tools make it easy to start improving your LLM workflows. A simple first step is to explore viral LLM tools and implement basic observability using OTEL-compatible telemetry. This approach helps you monitor real-world inputs and outputs, giving you valuable insights before diving into more complex evaluation systems. OpenAI emphasizes the importance of this process:
"If you are building with LLMs, creating high quality evals is one of the most impactful things you can do. Without evals, it can be very difficult and time intensive to understand how different model versions might affect your use case".
For teams prioritizing production reliability, tools like Latitude offer an end-to-end workflow for observability and prompt optimization. With an open-source version for self-hosting and paid plans starting at $299/month, Latitude provides a structured approach to reducing critical errors by 80% and iterating eight times faster. Meanwhile, academic teams can rely on tools like LM Evaluation Harness and Lighteval for standardized benchmarking across hundreds of tasks. The key is to choose the right tool for your goals, whether you're focused on catching production errors, comparing model versions, or ensuring your AI features meet quality standards before deployment.
FAQs
How do open-source platforms help reduce errors in large language models during production?
Open-source platforms play a key role in spotting and fixing issues in large language models (LLMs) before they reach end users. With tools like reusable test suites, automated metrics, and version-controlled benchmarks, these platforms empower developers to identify problems such as hallucinations, bias, or prompt drift early in the development cycle. Many of these platforms also integrate seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines, ensuring that any failed evaluations halt deployments and offer actionable insights for improvement.
Take Latitude, for instance - it enables teams to track critical errors, refine prompts swiftly, and drastically cut down on production failures. These platforms establish a strong feedback loop, helping teams build more dependable and precise LLM-powered products at scale.
What are the key advantages of using Latitude for evaluating large language models?
Latitude streamlines the process of working with large language models (LLMs) by offering tools designed to help you craft, test, and refine prompts efficiently. With its Prompt Manager, you can build advanced templates, run multiple experiments at once, and automatically gather results for deeper analysis. The platform also supports a variety of evaluation methods, such as using LLMs as judges, incorporating human reviews, and comparing outputs against ground-truth data - all while keeping version-controlled logs to track every step.
By treating prompts as version-controlled assets, Latitude ensures that every adjustment is documented and ready for production, minimizing the chance of errors. Teams using Latitude have reported impressive results: an 80% drop in critical errors, an 8× boost in prompt iteration speed, and a 25% increase in accuracy in just a few weeks. These improvements translate to faster testing, more dependable AI models, and greater trust in overall performance.
Why should you use open-source tools to evaluate large language models (LLMs)?
Open-source tools play a key role in evaluating LLMs, offering transparency, reproducibility, and the opportunity for community-driven improvements. By providing open access to code and benchmark data, these tools allow anyone to verify results, spot potential issues in implementation, and contribute to refining evaluation methods. This openness helps ensure assessments are both fair and dependable.
Another advantage of open-source platforms is their ability to reduce costs while offering flexibility. Teams can tailor these tools to meet specific requirements, seamlessly integrate them into existing workflows, and foster collaboration across different roles. For instance, Latitude enables engineers and domain experts to work together in creating production-ready LLM features, aligning evaluations with practical, real-world use cases. Leveraging open-source tools allows organizations to develop reliable, high-performing models without worrying about hidden expenses or limitations.

